Multi-joint exercises with dumbbells. Basic exercises for gaining muscle mass. Basic exercises with a barbell
In bodybuilding there are different kinds exercises that can be divided into:
- multi-joint– work with a barbell, free weight, body weight;
- isolated– work on simulators, blocks, frames.
They differ from each other in that the first are basic exercises for gaining weight, and the second are grinding/polishing, cutting out specific parts from the total volume of the mass.
The classic basic exercises in powerlifting are:
There are more basic exercises in bodybuilding; a complete list of basic exercises by muscle group in bodybuilding is presented below.

The bench press is a basic free weight exercise. To perform it, lie down on a bench, lower the barbell until it touches your chest, and then raise it until the elbow joint is fully straightened. The grip should be wide enough, wider than shoulder width. In bodybuilding, the bench press is used as an exercise to develop the muscles of the chest, triceps, and anterior deltoids.
Bench press incline bench allows you to work the upper sections of the chest muscles (if performed in the head-over-legs position) or their lower sections (if performed in the head-down position).
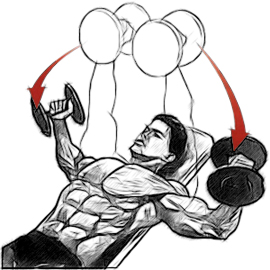
When pressing dumbbells, the lowest point of movement is much lower than when pressing a barbell, which allows you to perfectly work the pectoral muscles. In addition, you can change the trajectory of movement, squeeze dumbbells located in parallel, bring them together at the top point, which engages new muscle bundles and has a slightly different effect on them.
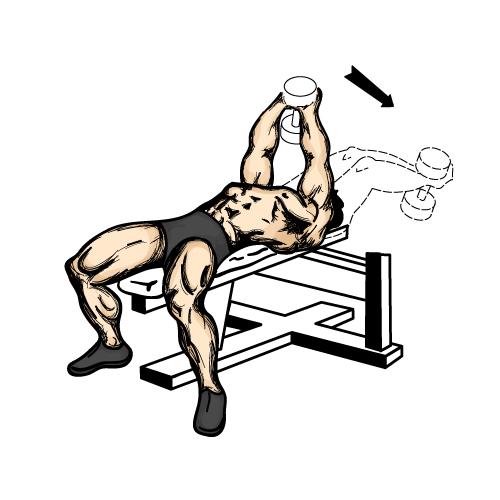
Due to the fact that lying dumbbell flyes involve the same muscles as the bench press, the load is focused on the inner edge and middle of the pectoralis major muscle. In this case, the chest is given a convex shape, a clear separation between its muscles is achieved. Routing is also done to improve the relief pectoral muscles By performing this exercise you can improve your results in wrestling, tennis, boxing, gymnastics, acrobatics, basketball, badminton.
This auxiliary exercise is aimed primarily at strengthening the pectoral muscles, latissimus muscles back and, indirectly, triceps. Pullover is usually performed as additional exercise when working on the pectoral muscles.

One of the main exercises to strengthen the back muscles. To perform, you need a horizontal bar or crossbar, which is easy to make even at home. This is the simplest exercise, but its value lies in the fact that it is basic and allows you to use a large number of different muscle groups.
As a compound movement, the deadlift involves almost every muscle, either to stabilize the position or to lift the weight. This exercise is used to build strength and mass in the muscles of the legs, back, and indeed the whole body.
By regularly performing this exercise, you can develop the latissimus, teres major muscles, and also influence a number of others, which will allow you to achieve visual and actual thickening of your back. This exercise is used as a supplement to various options deadlift in order to fully work out the back muscles.
This exercise allows you to create an aesthetic V-shaped torso. In this case, the arms should not go back, but move strictly in the plane of the body. The grip should not be wide; it is optimal when the forearm is perpendicular to the bar at the lowest point. The back should bend and the legs should be supported.

already described above
The barbell squat primarily engages the quadriceps, which are synergists (helping with movement) in in this case are gluteal muscles, soleus muscles along with the adductor muscles of the thigh. The calf and thigh muscles act as stabilizers. The back extensors and muscles also work abdominals and others.
The exercise is great for developing calf muscles. You can perform it both sitting and standing. For achievement best result It is reasonable to combine both options.

Performance this exercise requires very simple equipment - beams. You can find them in almost any yard, not to mention gyms. For the development of the triceps and pectoral muscles, this is perhaps the best exercise. This also applies to a large number of auxiliary muscles located in the shoulder girdle. Push-ups allow you to effectively work out your triceps and chest, but the degree of load depends on the position of your arms.
In order to increase the strength and volume of the triceps, use French press. It affects all triceps bundles, especially the upper and long ones. This also allows you to visually increase the volume of your arm.
To develop top part triceps and increase its strength and volume, it is worth using the bench press narrow grip. Moreover, despite the highest working weight compared to other triceps exercises, this exercise is used, as a rule, as a supplement to pumping up the triceps. The reason is simple: in addition to the triceps, the front deltoids and the upper pectoral muscles work. Another advantage of the close-grip bench press is that you can really work on the shape of your triceps. When this muscle goes into failure, and the performer continues the exercise with the help of the anterior deltoids and chest muscles, it is these repetitions that allow for excellent grinding of the triceps.
You can increase strength and mass in your biceps with this basic exercise. The load is distributed evenly across both biceps and muscles inner surface forearm and brachialis muscles.
If you change the grip width, you can shift the load to different biceps bundles. The narrower the grip, the more the internal beams work. And vice versa.
In order to develop biceps muscle The shoulder and forearm are used to lift dumbbells for biceps. The exercise involves turning your hands outward while lifting. This allows you to achieve maximum contraction of the biceps and synergistic muscles. For training the biceps, this exercise is considered one of the best, since turning the palm when bending the elbow adds efficiency.

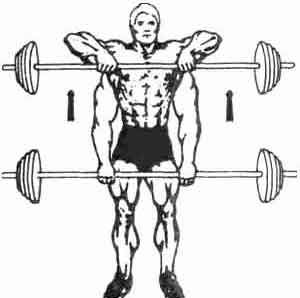
Most bodybuilders use this basic exercise to develop shoulder girdle. It perfectly loads the middle and front deltoids, as well as the upper part of the trapezius muscles.
To develop the triceps and shoulder girdle muscles, it is recommended to perform dumbbell or barbell overhead presses in a standing position. Here the main load falls on the deltoid muscles, with the main emphasis on the anterior section, as well as the triceps.
With the help of this exercise, pumping occurs rear delts, rotator cuff muscles and trapezius muscles. Bent-over dumbbell raises are best for developing the shape and definition of the deltoid muscles.
The exercise is suitable for working the middle deltas, upper and middle trapezius. Also, pulling to the chin separates the trapezius from the deltoids, allowing you to draw and sharpen the shape trapezius muscles, and also outline a clear line between the deltas and the trapezoid.
Shrugs are used to develop the trapezius muscle. The exercise is quite simple: holding the weight in straight arms, lowered along the body, raise the shoulders as high as possible, then lower the shoulders back without bending the arm at the elbow. Shrugs are usually performed with weights, dumbbells, barbells, or on a special machine. In this case, the bar can be placed both in front of the hips and behind the body.
Basic exercises and technique - Video
Physiological classification of physical exercises
In your daily activities - at home, at work, during classes physical culture and sports - a person performs a wide variety of motor actions: From a physiological point of view, a set of motor actions (movements) continuously connected with each other, aimed at achieving a specific goal (solving a motor problem), is an exercise.
In a competitive sports exercise, a set of motor actions (movements) is aimed at achieving the maximum possible sports result (examples sports exercises: high jump, javelin throwing, shooting, sports game, running or swimming over a certain distance).
A huge number of physical, including sports, exercises necessitate their classification. Physiological classification combines into groups physical exercise with similar functional characteristics. On the one hand, these are exercises for the successful implementation of which, to a certain extent, similar modes, means and methods can be used physical education(sports training). On the other hand, one group combines physical exercises that can be equally used in the physical education system ( sports training) to increase the functionality of the same physiological organs, systems and mechanisms, and, consequently, the same physical quality. Thus, the possibilities of cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which largely determine the level of endurance development, can be successfully increased by using different physical exercises of the same group: long running, cycling, swimming, cross-country skiing.
General physiological classification of physical exercises
The most general physiological classification of physical exercises can be carried out on the basis of identifying three main characteristics of the activity of the muscles performing the corresponding exercise:
1) active volume muscle mass;
2) type muscle contractions(static or dynamic);
3) strength or power of contractions.
Local, regional and global exercises
Depending on the volume of active muscle mass, all physical exercises are classified into local, regional and global.
Local exercises include exercises in which less than 1/3 of the total muscle mass of the body is involved (archery, pistol shooting, certain gymnastic exercises).
Regional exercises include exercises in which approximately 1/3 to 1/4 of the total muscle mass of the body is involved (gymnastic exercises performed only by the muscles of the arms and waist upper limbs, trunk muscles, etc.).
Multi-joint exercises cause the greatest hormonal response. For this reason, they are effective for gaining weight. Learn about new discoveries in fitness.
If you focus on basic movements, you will definitely progress. This applies not only to weight gain, but also to strength parameters. For example, if you do squats, the progress will be much greater than if you replace it with others.
Technique for performing a chest push while standing in fitness

This is an excellent movement for developing the muscles of the shoulder, legs and back. On average, an athlete can gain more than ten kilos of quality mass in a year thanks to the chest press. Of course, for this it is necessary to perform it in strict accordance with the technique and take it seriously.
This movement is quite popular in weightlifting, where it is divided into two phases when performed. First you need to lift the projectile onto your chest, thereby working the muscles of the legs and back, and then perform a push for the shoulder girdle. Now we will talk about the technique of this magnificent movement.
Stage 1
Squat down into the position you want to take when performing a deadlift. The only difference is the grip. In this case, it is necessary to use a different grip. Make sure your back is straight and there is a natural arch in your lower back. Lift the projectile using only the force of your legs. After the bar passes the knee joints, detonate the projectile.
Stage 2
Straighten your body and use your shoulders to give the projectile momentum to move upward.
Stage 3
Turn your hands and sit under the projectile. Be careful, as the bar may already begin to move downwards. After taking the projectile to your chest, straighten up completely.
Stage 4
Bend your knees and push upward, working not only with your arms, but also with your legs. Raise the apparatus above your head and lower the barbell. The entire movement is performed without pauses between stages.
Exercises for leg muscles

All athletes know how difficult it is to build leg muscles. Almost no one likes it, but they need to be trained. In most cases, in beginners, the leg muscles are poorly developed and this is due to several reasons. But now we won’t talk about them, but will give advice on how to quickly pump up your legs.
- Try to work on your leg muscles on the first training day of each week and dedicate a separate session for this.
- It is better to pump the quadriceps using the pumping effect, which means performing 12 to 15 repetitions per set. For the muscles of the buttocks and hamstrings, it is better to use a small number of repetitions, from 4 to 6, and work with heavy weight.
- At the end of each training week, pay special attention to your hamstrings.
- Find time to do specific leg training once a week.
- This class requires you to jump on high pedestals, perform sprints at a powerful pace, and jump up and forward.
Bench press exercise

Many pro-athletes have noticed that when performing a bench press, the muscles of the upper back are in a state of static tension. This helps improve hand stabilization. The triceps are subjected to a similar load in the initial phase of movement, thereby helping to maintain elbow joints at an angle of 90 degrees.
To increase the load on these muscles, it is necessary to force them to contract intensively. This can be achieved by placing a ring-shaped rubber shock absorber on your wrists, twisting it in an “8” shape. Once the shock absorber is on your wrists, you can begin to press.
Deadlift exercise

This is an excellent exercise to perform for all athletes who want to achieve good results. At the same time, it is quite traumatic and you have probably heard about it. To a greater extent deadlift poses a danger to athletes with poorly developed lower back muscles. But this is an excellent exercise that still needs to be performed, for this reason we will now tell you how to reduce the risk of injury when performing it:
- The apparatus should be placed on supports just above the knee joints (this is advice for beginners).
- The initial working weight should not exceed half your body weight.
- Perform the movement no more than twice a week.
- Increase the weight by no more than 2 or 2.5 kilos. If the load turns out to be too much for you, reduce it.
- Don't work yourself to failure.
- After the working weight is equal to twice your body weight, lower the projectile down one division and again start with a weight of 0.5 of your body weight.
- Stick to this mode until the projectile is on the ground.
- When working with heavy weights, use a different grip.
It is necessary to lift the projectile from the ground (stops) slowly. Once the bar is in the air, increase the speed of the projectile, but do it smoothly. After the projectile passes the level of the knee joints, the speed of the bar should be maximum.
Kettlebells are a great addition to basic exercises.

You can significantly increase the effectiveness of basic exercises by using them in your training program weights Now we will tell you about the most effective exercises with this sports equipment, which will allow you to achieve the following effects:
- Eliminate fat reserves;
- Increase functional strength;
- Give the muscles relief.
Gladiator

Lean sideways on your outstretched arm, and lift your free leg up, keeping it suspended. Press the kettlebell with your free hand. After execution required quantity repeat the exercise in the other direction.
Kettlebell Squat Press

Lower yourself into a squat while holding sports equipment at arm's length above your head. The second hand holds the second weight located on the ground. As you rise from the squat, press the second kettlebell upward.
Lunges

Press the two weights upward and hold the weights in your straight arms. Maintaining this position, begin to lunge while walking. After walking ten meters, turn around and move back.
Why do athletes need basic exercises?

Although the effectiveness of basic movements has been proven not only by the many years of experience of a huge number of athletes, today you can increasingly come across the opinion that a base is not needed. The only exception here is the bench press, which is something you won't hear about. Here are the main reasons that make athletes refuse to perform squats, deadlifts, snatches, etc.
- Due to poor technique, you can get injured, because you have to work with heavy weights.
- Often athletes do not see progress from performing basic movements, which is again due to the lack of correct technique.
- Many bodybuilders believe that squats and deadlifts are most effective for powerlifters. With what's in powerlifting These exercises receive a lot of attention; it is useless to argue, but all pro-bodybuilders also use them during their training.
Find out more about interesting and unusual exercises in fitness from this video:

Lecture 1
Physiological classification of physical exercises
Plan:
1. Physiological classification of physical exercises
2. General physiological classification of physical exercises
2.1. Local, regional and global exercises
2.2. Static and dynamic exercises
2.3. Strength, speed-strength and endurance exercises
3. Energy characteristics of physical exercises
4. Physiological classification of sports exercises
4.1 Classification of cyclic exercises
4.2 Classification of acyclic exercises
Introduction to the subject.
Sports physiology is the second part of the physiology course studied at physical education institutes. The main content of this course is the physiology of human muscular activity, a special case of which is sports activity. In the course of sports physiology, two central issues can be distinguished - the physiological characteristics of various types of sports activities and the physiological mechanisms of adaptation of the body during sports training.
WITH athletic activity is associated, as a rule, with maximum or almost maximum tension of the leading physiological systems that ensure its implementation. The main task of sports physiology is to provide a quantitative description of the physiological reactions of individual systems and the entire organism for different types of sports activities.
IN in his daily activities - at home, at work, during physical education and sports - a person performs a wide variety of motor actions: From the point of view of physiology, a set of motor actions (movements) continuously interconnected with each other, aimed at achieving a specific goal (solving a motor problem ), is an exercise.
IN In a competitive sports exercise, a set of motor actions (movements) is aimed at achieving the highest possible sports result (examples of sports exercises: high jump, javelin throwing, shooting, sports game, running or swimming over a certain distance).
ABOUT The huge number of physical, including sports, exercises necessitates their classification. Physiological classification groups physical exercises with similar functional characteristics. On the one hand, these are exercises for the successful implementation of which, to a certain extent, similar regimes, means and methods of physical education (sports training) can be used. On the other hand, one group combines physical exercises that can be equally used in the system of physical education (sports training) to increase the functionality of the same physiological organs, systems and mechanisms, and therefore the same physical quality . Thus, the capabilities of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, which largely determine the level of endurance development, can be successfully increased by using different physical exercises of the same group: long running, cycling, swimming, cross-country skiing.
N The most general physiological classification of physical exercises can be carried out on the basis of identifying three main characteristics of muscle activity:
1 ) volume of active muscle mass;
2 ) type of muscle contraction (static or dynamic);
3 ) strength or power of contractions.
2.1. Local, regional and global exercises
IN Depending on the volume of active muscle mass, all physical exercises are classified into: local, regional and global.
TO local exercises include exercises in which less than 1/3 of the total muscle mass of the body is involved (archery, pistol shooting, certain gymnastic exercises).
TO Regional exercises include exercises in which approximately 1/3 to 1/4 of the total muscle mass of the body takes part (gymnastic exercises performed only by the muscles of the arms and the belt of the upper limbs, muscles of the torso, etc.).
G“Local” exercises are those in which more than 1/2 of the total muscle mass of the body is actively involved (running, rowing, cycling, etc.). The vast majority of sports exercises are global.
2.2. Static and dynamic exercises
IN According to the type of contraction of the main muscles performing this exercise, all physical exercises can be divided into static and dynamic, respectively.
TO static exercises include, for example, maintaining a fixed pose while holding a handstand (for gymnasts) at the moment of shooting (for a shooter).
B Most physical exercises are dynamic. These are all types of locomotion: walking, running, swimming, etc.
2.3. Strength, speed-strength and endurance exercises
At classification of physical exercises according to the force of contraction of the leading muscle groups, two dependencies should be taken into account: “strength - speed” and “strength - duration” of muscle contraction.IN According to the “force - speed” relationship (Fig. 1), during dynamic contraction the force exerted is inversely proportional to the speed of muscle shortening (the speed of movement of the moving part of the body): the greater this speed, the less the force exerted. Another formulation of this relationship: the greater the external load (resistance, weight), the lower the speed of shortening (movement) and the greater the manifested force, and vice versa, the smaller the external load, the higher the speed of movement and the less manifested muscle force. The product of force and the speed of muscle contraction determines its power (see Fig. 1).
Z The strength-duration relationship of muscle contractions is expressed in the fact that the greater the strength (or power) of muscle contractions, the shorter their maximum duration. This is true both for local and regional static and dynamic work (Fig. 2) and for global work (Fig. 3).
By Based on the strength and power of muscle contractions and the associated maximum duration of work, all physical exercises can be divided into three groups: strength, speed-strength (power) and endurance.
WITH silt exercises can be considered exercises with maximum or almost maximum tension of the main muscles, which they exhibit in a static or dynamic mode at low speed - movement (with large external resistance, weight). In Fig. 1 strength exercises corresponds to the left side of the force-velocity curve. The maximum duration of exercises with maximum manifestation of strength is calculated in several seconds. Strength is the main motor quality that determines the success of strength exercises.
WITH Core-strength (power) exercises are those dynamic exercises in which the leading muscles simultaneously exhibit relatively greater strength and speed of contraction, i.e., greater power. The maximum power of muscle contraction is achieved under conditions of maximum muscle activation at a shortening rate of about 30% of the maximum for an unloaded muscle. On the strength-velocity curve, speed-strength exercises occupy the middle position - up to 50-60% of maximum speed(see Fig. 1). Muscles develop maximum power with external resistance (load) that is 30-50% of their maximum (static) strength. The maximum duration of an exercise with high power of muscle contractions is in the range from 3-5 s to 1-2 minutes - in inverse proportion to the power of muscle contractions (load). Power plays a critical role in speed-strength exercises.U Endurance exercises are considered to be those exercises in which the leading muscles develop contractions that are not very strong in strength and speed, but are able to maintain or repeat them for a long time - from several minutes to many hours (in inverse proportion to the strength or power of muscle contractions) . Endurance - leading physical quality for the exercises of this group.
E Energy cost is the most important characteristic of the exercise. To determine the energy cost of physical exercise, two indicators are used: energy power and gross (total) energy consumption.
E energetic power is the amount of energy expended on average per unit of time when performing a given exercise. It is usually measured in physical units: watts, kcal/min, kilojoules per minute, as well as in “physiological”:
With rate of O2 consumption (ml O2/min) or in METs (metabolic equivalent), i.e. the amount of O2 consumed in 1 min per 1 kg of body weight under conditions of complete rest while lying down. 1 MET is equal to 3.5 ml O2/kg min).
IN total (total) energy expenditure is the amount of energy expended during the entire exercise as a whole. Gross energy expenditure (total energy cost of an exercise) can be defined as the product of average energy output and the duration of the exercise.
At When running, the gross energy consumption to cover the same distance, within certain limits, does not depend on the speed of movement. The fact is that with an increase in speed (energy power), the time to cover a given distance decreases, and with a decrease in speed, on the contrary, it increases, so that the product of energy power and time, i.e., the total energy consumption, remains unchanged. The total energy cost of covering the same distance is higher when running than when walking (up to a speed of about 8 km/h): for each kilometer of walking distance, an average of 0.72 kcal/kg of body weight is consumed in women and 0.68 kcal /kg body weight in men, and when running, 1.08 and 0.98 kcal/kg body weight, respectively.
By In terms of energy capacity, physical exercise is usually divided into light, moderate (medium), heavy and very heavy (Table 1).
Table 1. Classification of physical exercises by energy expenditure (kcal/min) in men and women of different ages.
|
Gender and age |
Exercises |
|||
|
moderate (average) |
very heavy |
|||
At When assessing the severity of an exercise based on energy indicators, it is necessary to take into account a number of factors: the nature of the work performed (static or dynamic), the volume of active muscle mass (local, regional or global exercise), body size or weight, age, gender and degree of fitness (physical fitness) the person performing this exercise, the external conditions for performing this exercise.
T So, if very hard local work is performed, which can last only a few tens of seconds, the rate of energy expenditure of the body does not exceed 1.2 kcal/min (Table 2). The same rate of energy consumption is typical for regional work of moderate (moderate) severity, which can be performed for many tens of minutes, and for global, but very light work (extremely slow walking on level ground), which lasts for many days in a row. Very heavy global work for women aged 50-59 years with an energy expenditure of more than 5.5 kcal/min, which can last only tens of seconds, is moderate for men 20-29 years old and can be performed by them for several hours (see table . 1).
Table 2. Classification of the severity of local, regional and global exercises by energy expenditure (kcal/min)
ABOUT Particularly large differences in the energetic assessment of exercise severity exist between untrained people and highly trained athletes. The latter are able to perform loads with such energy costs that are inaccessible to untrained people. For athletes in the vast majority of sports, the severity of physical exercise in terms of energy (and other) indicators exceeds heavy or even very heavy loads for untrained people and is inaccessible to the latter (Table 3).
Table 3. Energy cost of various types of physical education and sports activities (according to E. M. Berkovich, N. V. Zimkin, N. I. Volkov, etc.)
|
Kind of activity |
Energy cost.(kcal/min) |
|
Rest: lying down | |
|
18 km/h (5.0 m/s)** | |
|
23 km/h (6.3 m/s)*** | |
|
26 km/h (7.2 m/s) **** | |
|
32 km/h (8.8 m/s)***** | |
|
Swimming: | |
|
crawl 0.9 m/s | |
|
on the back 0.6 m/s | |
|
breaststroke 0.8 m/s | |
|
Skiing 13 km/h | |
|
Ice skating | |
|
A ride on the bicycle | |
|
more than 30 km/h | |
|
Gymnastics | |
|
trunk flexion | |
|
turns on the crossbar, | |
|
Volleyball (recreational) | |
|
single | |
|
Sport games | |
|
(football, basketball, handball) |
* Corresponds to jogging speed. ** Corresponds to the speed of marathon running with a result of 2 hours. 20 minutes. *** Corresponds to the running speed of 10,000 m with a result of about 28 minutes. **** Corresponds to a running speed of 1500 m with a result of about 3 min 40 s. ***** Corresponds to the running speed of 400 m with a result of 45 s.
WITH From a physiological point of view, the severity of the same physical exercise varies greatly depending on the conditions of its implementation (for example, in the mountains or at elevated temperatures and humidity), although its energy cost remains almost or completely the same as under normal conditions.
T Thus, assessing the severity of an exercise using energy criteria alone is insufficient. Therefore, many classifications of physical exercises, along with energy characteristics (related to weight or body surface), also take into account a number of other physiological indicators (Table 4): rate of O2 consumption, heart rate (HR), pulmonary ventilation (PV), body temperature, respiratory coefficient (DC), lactic acid content in the blood, etc.
Table 4. Classification of physical work by energy and physiological indicators (based on data from untrained men)
|
Difficulty of work |
Energy capacity |
Physiological indicators |
Type of activity (working time limit) |
||||||||
|
kcal/min* |
VO2 ML/KG*MIN |
VO2***, l/min |
Heart rate, beats/min |
Rectal temperature |
Blood lactate, mg% | ||||||
|
Easy job: | |||||||||||
|
calm |
Indefinitely |
||||||||||
|
moderate |
Normal work activity (up to 8 hours per day) |
||||||||||
|
Average performance: optimal |
Intensive work activity (8 hours a day for several weeks - seasonal work) |
||||||||||
|
Hard work: intense |
Physical education classes (1 - 2 hours a day, 3 times a week) |
||||||||||
|
Very hard work: | |||||||||||
|
maximum |
Intense training (up to 1-2 hours per day) |
||||||||||
|
exhausting |
Competitive exercise (several minutes) |
||||||||||
1 kcal/min = 426.85 kgm/min = 69.767 Watt = 4.186 kJ/min. ** 1 MET = 3.5 ml, O2/kg*min - 0.0175 kcal/kg = 0.0732 KJ/kg. *** 1 l of O2 consumption = -5.05 kcal = 21.237 kJ
The main exercises in the HIT system can be divided into two categories: single-joint and multi-joint. In single-joint exercises, as you can guess, only one joint (or two identical joints on different limbs) is involved. These include, for example, raising arms with dumbbells, since this movement involves only shoulder joints. A good example of a multi-joint exercise is the overhead press because the movement involves the joints of the shoulders, elbows and wrists.
Both types of exercise are important for building muscle, but for different reasons. The single-joint movement is much better at isolating a specific muscle group, such as the deltoids in the dumbbell fly example. In a multi-joint exercise, different muscle groups do specific work, although none of them receives full load. The overhead barbell press targets your triceps, deltoids, and trapezius muscles, but none of these muscle groups go through a full range of motion. To do this, you need good extensions for the triceps, raises with dumbbells or on a deltoid machine, and shrugs for the trapezius muscles.
But this does not mean that the overhead press is an inferior exercise. It activates more muscle mass than any single-joint exercise. This means you can work with a much higher load and achieve faster muscle growth.
So, one type of exercise is designed to increase overall muscle mass, and another type of exercise is designed to train and develop individual muscles when they are subjected to stress through the maximum range of motion. The right combination of these exercises forms the best training routine.
Best Single Joint Exercises
The Best Multi-Joint Exercises
Dumbbell presses on horizontal bench
Best exercises second echelon
Exercises to avoid
The following exercises are not safe and are recommended to be avoided:
Clean and jerk
Dumbbell push
Barbell Snatch
Snatch with dumbbells
Lunges with dumbbells
Jumping squats with dumbbells
Front squats with barbell
"Bridge" with a barbell
The clean and jerk, the snatch, and the two-arm barbell press are popular exercises among Olympic weightlifters and are essential in their training, as these movements with the heaviest implements are part of their competition program. However, the explosive nature of such exercises places enormous stress on the working muscles, joints and connective tissues. In addition, in all these exercises the inertia of movement is too great. so that they can serve to effectively build muscle mass. Some football coaches recommend that players do push exercises with barbells, but this does not benefit the football players. Refrain from these and any other exercises with a sharp, explosive nature of movement.
Lunges with a barbell or dumbbells are another dangerous exercise. Reciprocating with a heavy weight creates too much inertia. Plus, barbell squats are more effective and much safer.
Jumping squats with dumbbells is another risky exercise. A sharp straightening with pushing off the floor threatens ligament sprains and traumatic damage to muscle tissue.
Barbell front squats are uncomfortable and limit mobility because the barbell sits above your collarbones during the movement. Regular barbell squats are again more effective.
The “bridge” with a barbell across the chest is a favorite exercise of many wrestlers. However, doing this creates too much pressure on cervical region spine. Special simulators for neck muscles, the Nautilus, Hammer and MedX brands are better suited for this purpose.