Frequency of strength training. Short and infrequent workouts: why they are effective and who is suitable for them. Training frequency for gaining weight
What will unsettle you, or you will simply hit the ceiling. Training should bring benefits to the body, but not harm, and for this, the optimal frequency of training per week, a clear plan and schedule should be chosen. In this article we will try to determine the optimal frequency of training per week for the best progress.
How often should you exercise to grow muscles?
 Most experts say that weight training shouldn't be done every day because it creates micro-tears in the muscle fibers, and the muscles then need 24 to 48 hours of rest to repair themselves and get stronger. But in fact, it all depends on many factors, such as: gender, age, what weight you exercise, how you recover, whether you use additional medications, etc. If we take into account the general recommendations while observing all the rules of progress, then train each muscle group no more than 2 times a week and no less than 1 time every two weeks! And then everything depends on the method you choose and on the correctly drawn up plan.
Most experts say that weight training shouldn't be done every day because it creates micro-tears in the muscle fibers, and the muscles then need 24 to 48 hours of rest to repair themselves and get stronger. But in fact, it all depends on many factors, such as: gender, age, what weight you exercise, how you recover, whether you use additional medications, etc. If we take into account the general recommendations while observing all the rules of progress, then train each muscle group no more than 2 times a week and no less than 1 time every two weeks! And then everything depends on the method you choose and on the correctly drawn up plan. 

The optimal value here would be around 3-5 workouts per week, depending on the split you choose. Beginners are recommended to train 2 times a week (conditionally dividing the whole body in half). And for more advanced people and those who use pharmacology, you can train 6-12 times a week, i.e. Conduct 2 workouts a day (strength + cardio). But again, everything depends not on quantity, but on quality, i.e. you should become bigger and stronger with each workout, but not vice versa, and for this you need to train yourself and your body to (constantly) grow intelligently and achieve the effect of supercompensation.
How often should you exercise to lose weight?

 – these are, first of all, questions, i.e. The total calorie content of food eaten per day should be lower than your daily expenses. You should spend 300-500 calories more than you eat to lose weight. And the rate of weight loss should not exceed 1 kg per week, otherwise you will lose precious muscles along with fat.
– these are, first of all, questions, i.e. The total calorie content of food eaten per day should be lower than your daily expenses. You should spend 300-500 calories more than you eat to lose weight. And the rate of weight loss should not exceed 1 kg per week, otherwise you will lose precious muscles along with fat.
Well, as for the issue of training frequency, for weight loss it is recommended to do them at least 3 times a week; these should be mainly low-intensity cardio training lasting about 1 hour. If you train in the gym, then after strength training it is recommended to spend 30 minutes. cardio, which will give a significant fat-burning effect .
How often can you do cardio workouts?

 good for strengthening the heart, losing weight and relieving depression. Brisk walking, swimming, aerobics, elliptical training or moderate cycling should not strain the muscles for too long (more than 60 minutes), otherwise this can lead to catabolic processes, i.e. muscle loss.
good for strengthening the heart, losing weight and relieving depression. Brisk walking, swimming, aerobics, elliptical training or moderate cycling should not strain the muscles for too long (more than 60 minutes), otherwise this can lead to catabolic processes, i.e. muscle loss.
If you combine cardio and strength training, then for this approach it is recommended to do cardio training 3 times a week, taking into account 3 strength training sessions. If we talk about low-intensity cardio, then you can train up to 6-7 times a week, and for high-intensity cardio, spend no more than 3 days a week.
How often do stretching/stretching?

 The frequency of exercise is always determined by the intensity of the loads themselves, i.e. it all depends on which stretching method you use (there are about 11 in total). If you use simple methods like passive and static stretching (the most popular in general), then the optimal frequency of training is daily training, and even more optimal is 2 times a day, but with less volume. For example, if you stretch every day for an hour, then switching to 2 times a day, you need to do a morning workout of 30 minutes, and an evening workout of 20 minutes, or vice versa.
The frequency of exercise is always determined by the intensity of the loads themselves, i.e. it all depends on which stretching method you use (there are about 11 in total). If you use simple methods like passive and static stretching (the most popular in general), then the optimal frequency of training is daily training, and even more optimal is 2 times a day, but with less volume. For example, if you stretch every day for an hour, then switching to 2 times a day, you need to do a morning workout of 30 minutes, and an evening workout of 20 minutes, or vice versa.
Do stretching at least 2-3 times, and ideally train 5-7 times a week.
Day of rest
Give yourself at least one official day off a week from any physical activity and daily routine work. Such a day will only benefit not only your body, but will also allow you to relax mentally and emotionally. But if you want to make your day off more functional and spend it beneficial for your body and body, then you can simply take a walk, which is very beneficial for a person.
The optimal frequency of training per week is determined, first of all, by the main purpose of visiting the gym - from building muscle mass for men, to training for fat burning and maintaining good physical shape for women. It is the goal factor that determines how many days of proper rest the body will need to recover.
If long-term, but relatively light, cardio training for burning fat can be done 4-5 times a week, then strength training for the purpose of muscle growth will require more recovery time. That is why the most effective training frequency for muscle growth is 3-4 visits to the gym per week. We also talked about that.
On the other hand, the answer to the question of how many times a week you can train, in many cases, is related to your life schedule. In most cases, people find it more convenient to go to the gym 3 times a week - usually Monday, Wednesday and Friday. It is according to this schedule that the three-day split is built and.
How long does it take for muscles to recover?
Scientific research suggests that the time required for muscle recovery after exercise is on average 48 to 72 hours - or 2 to 3 days. In reality, this figure depends both on the level of experience of the athlete and his age (the older the person, the longer the recovery takes), and on which muscles were involved in the training.
Moreover, if small and medium muscle groups (for example, arms, shoulders and abs) require about 48 - 60 hours for regeneration, then for the full restoration of large muscles (primarily legs, chest, back), and, in particular, the central nervous system , also experiencing severe stress when performing basic exercises, needs at least 72 hours (1).
Recovery time for muscle groups
| Shoulders | 48 – 60 hours |
| Breast | up to 72 hours |
| Back | up to 72 hours |
| Press | 48 – 60 hours |
| Triceps | 48 – 60 hours |
| Biceps | 48 – 60 hours |
| Buttocks | up to 72 hours |
| Thigh muscles | up to 72 hours |
| Caviar | 48 – 60 hours |

It is traditionally believed that specific “pulling” pain in the muscles after playing sports is directly related to their growth. From a scientific point of view, this is not entirely true, and muscle growth can occur without pain at all - it all depends on the individual characteristics of a person’s metabolism. Let us also note that sports significantly reduce this pain.
In fact, the specific “delayed” pain felt in the muscles of the body after performing heavy strength exercises simply means that the body is successfully repairing muscles and eliminating toxins formed after training (including). Typically, this pain begins 12 to 24 hours after exercise and ends completely within 24 to 72 hours.
Recovery after sports
Oddly enough, complete rest is not at all the optimal way to quickly restore the body after training. Research shows that moderate physical activity on days off from gym training increases blood flow and the rate of elimination of toxins, thus significantly accelerating the processes of regeneration and growth of muscle tissue.
In other words, light cardio done for 20-25 minutes on non-strength training days will not only speed up recovery, but will ultimately allow you to train more effectively for muscle growth and definition. A visit to the pool will also be useful - it’s no secret that swimming perfectly develops the body.
How many times a week should you pump your legs?

The legs are one of the largest muscle groups in the body, so it is recommended to train them no more than once every 72 hours - in other words, if you did heavy barbell squats on Monday, it is better to train your legs on Thursday or even Friday. However, if you trained exclusively calves or inner thigh muscles, then the time is reduced.
At the same time, the final number of days required to restore leg muscles also depends on the person’s body type - they can train more often (and, ultimately, build muscle faster), while the body either requires an increased amount of time to replenish energy reserves.
How often can you train your abs?
For beginners, in the first months of strength training, you can pump up your abdominal muscles 5 times a week - the presence of “delayed” pain will help you literally feel your abdominal muscles, which will dramatically increase the effectiveness of your abdominal training. However, we are talking about performing single exercises without additional load or simple training at home.
Complete sets of exercises for developing abdominal muscles will require about 48-60 hours for recovery. Separately, we note that more frequent training of the abdominal muscles is absolutely not able to remove fat from the abdomen faster (this requires only a diet). In fact, they will only cause overtraining and negatively affect overall progress.
How many times a week should girls train?
Speaking about training for fat burning, it is important to mention aerobic training for girls. In their case, daily training while reducing calorie intake can give the opposite effect to the desired one. Instead of speeding up metabolism and losing weight, the body can increase the level of the stress hormone cortisol, thus provoking not fat loss at all, but fat gain.
Losing weight should always begin with normalizing your diet and eliminating excessively high-calorie foods. Physical training for fat burning in this case is only a way to normalize metabolism and equalize blood sugar levels, and not at all a mechanism for getting rid of excess calories and directly “burning” fat.
***
Since the total time for muscle recovery is 48 hours for small muscle groups (arms, abs) and 72 hours for large ones (legs, chest), strength training for gaining mass is recommended 3-4 times a week. Training for weight loss can be done more frequently (up to 5 times a week), but without a sharp reduction in caloric intake.
Scientific sources:
- The Truth About Muscle Recovery Time,
Frequency and volume of training are the 2 key parameters that most influence the growth of muscle mass and strength and improvement of athletic performance. We have compiled translations of 2 texts about training frequency into this one - for your convenience (and we also like to work out quality work).
Until recently, it was believed that high-volume training of each muscle group once a week was optimal for gaining weight. New research shows that spreading your training volume over several sessions per week (i.e. increasing the frequency) is more effective. Moreover, frequent training becomes a necessity as you gain experience. Why? Due to muscle protein synthesis.
Protein synthesis and hypertrophy
Today, most scientists associate muscle hypertrophy with the process of muscle protein synthesis (1). After a workout in which the muscles experience sufficient stress, the level of synthesis increases: the body assembles new proteins from amino acids, that is, new muscle tissue.
But the duration of the period of increased synthesis differs between beginners and experienced trainees. Research shows that for beginners, synthesis processes can last two days ; Simply put, after each workout they can grow for 2-3 days (2).
Recent experiments, on the other hand, have found that in experienced athletes (accustomed to training loads), the growth period is reduced, reaching some 16 hours (3).
This is one of the main reasons for the slowdown in the rate of hypertrophy in trained people - and a reason to increase the frequency of visits to the gym. While a beginner can grow just fine by working a muscle group once a week, for an experienced athlete this is not far from the most effective strategy.
How much worse is a split than a round robin: a 2018 study among experienced athletes
Researchers (4) took 23 athletes of average fitness level. Their average result in the squat was ~165% of their body weight, and in the bench press ~130% of their body weight. The subjects were randomly divided into 2 groups: very high and very low frequency of exercise.
Both groups trained from Monday to Friday and did the same 11 exercises with the same load (70-80% of ) and the same number of sets (about 15 for each muscle group per week) until muscle failure. That is the volume and number of exercises in the groups were the same throughout the week.
The difference was this: low frequency group I did these exercises in a split mode - each muscle group was trained once a week. And the high-frequency group distributed exercises so as to load each muscle group in each workout.
In fact, it turned out that the group with a low frequency of load during training performed only 2 exercises, but in 5-10 working approaches, and the group with a high frequency did the opposite: they did 11 exercises, but only in 1-2 approaches each. Let us remember that the total number of approaches and exercises per week was the same.
Here's how the groups trained:
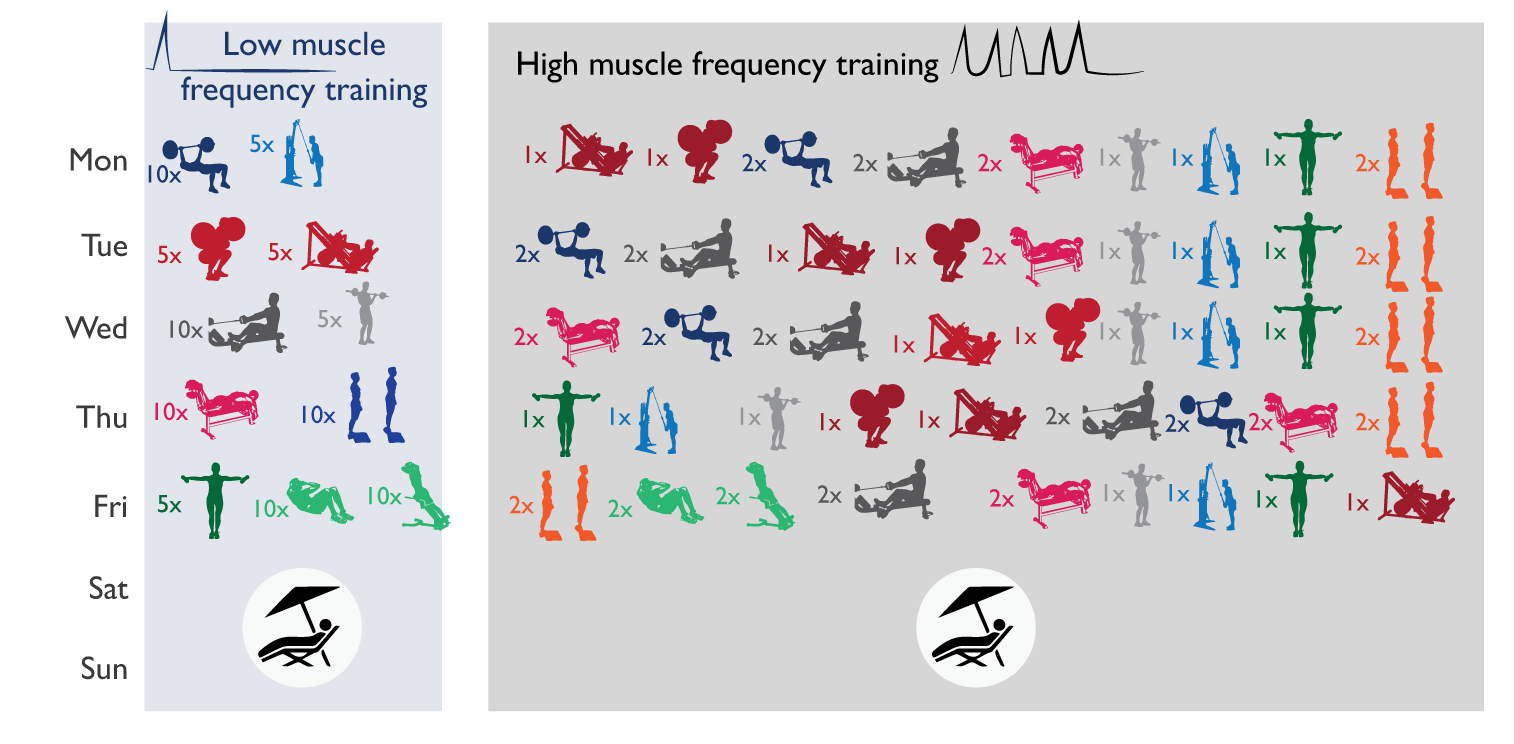
Left: the group with a low frequency of training muscle groups did 2 exercises, but 5-10 approaches in each. And the high frequency group did more exercises, but only 1-2 sets each.
And here are the results: both groups of participants gained strength and mass - without a statistically significant difference. However, If we look at absolute numbers, the high-frequency group still achieved more . Since the experiment lasted only 8 weeks, it can be assumed that in the long term the difference would be more noticeable.

Comparison of groups according to different indicators (from left to right): 1. Growth of lean muscle mass. 2. Increased strength in the bench press. 3. Increased strength in squats.
Another interesting finding was that the low-frequency group suffered significantly more from post-workout pain caused by infrequent high-volume workouts, but performed slightly worse.
Thus, more significant microtrauma did not lead to greater hypertrophy. Namely because of the pain Many people mistakenly prefer split training, believing microtrauma to be an indicator of the quality of training. Because of this, they cannot work out a muscle group more than once a week, selecting the frequency according to sensations, that is, according to misconceptions = throwance.
Benefits of increased frequency
By working a muscle group more often, you will, of course, reduce the number of working approaches in each individual workout, but you will gradually increase the total volume over the week.
Let's say at the very beginning of your training you loaded your legs once a week, performing 8 sets of squats. After which the muscles probably hurt for several days (but at the same time they grew). When we gain experience and get used to the loads, anabolic reactions after the same workout can end the very next day. It is clear that the intensity of an advanced athlete will be much higher, but still, after a day, growth will stop.
Let's divide the same volume into 2 workouts: 4 working sets of squats twice a week. Firstly, you will be able to train more intensely, recovering more easily after each session. Secondly, the leg muscles are worked more often (and protein synthesis increases more often), and - which is also important for hypertrophy - you can vary the exercises, for example, 4 sets of squats in one workout, and 4 sets of leg presses in another. All this only contributes to gaining muscle mass.
How to increase the frequency correctly
Of course, you need to increase the frequency wisely and in due time. If you have recently started training, then work according to your regular program for at least the first 4-6 months.
When you gain experience and muscle growth slows down, increase the frequency gradually:
- Do not immediately double the frequency of working out the muscles of the whole body. Move one at a time, gradually adding a second workout for each muscle group. This will reduce the risk of injury and not impair recovery.
- Reduce the volume of each workout; you can't just start doing the same 10 sets of squats twice a week. Distribute this volume over 2 sessions and vary the exercises.
- If you are recovering well, increase your total weekly volume in small steps by doing more work sets or further increasing the frequency.
In any case - no matter what experience you have - always listen to your body and do not overwork. Muscle growth is stimulated by training load, but is largely dependent on your recovery abilities. If you do too much (or too often), you will quickly overtrain.
Scientific sources:
1. Atherton, P. J., & Smith, K. (2012). Muscle protein synthesis in response to nutrition and exercise. The Journal of physiology, 590(5), 1049-1057.
2. Phillips SM, Tipton KD, Aarsland A, Wolf SE, Wolfe RR. Mixed muscle protein synthesis and breakdown after resistance exercise in humans. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 273: E99–E107, 1997.
3. Tang, J. E., Perco, J. G., Moore, D. R., Wilkinson, S. B., & Phillips, S. M. (2008). Resistance training alters the response of fed state mixed muscle protein synthesis in young men. American Journal of Physiology-Regulatory, Integrative and Comparative Physiology, 294(1), R172-R178.
4. High-frequency resistance training is not more effective than low-frequency resistance training in increasing muscle mass and strength in well-trained men. Gomes GK, Franco CM, Nunes PRP, Orsatti FL. J Strength Cond Res. 2018 Feb 27. doi: 10.1519/JSC.0000000000002559.
Correctly calculating the optimal frequency of training is not as simple as it might seem at first glance. This must be done depending on whether you are exercising to increase muscle mass or to lose weight. After all, glycogen is restored literally within a few hours after training, and muscle structures need several days.
Theoretical information
For a person working out to build muscle, it is advisable to conduct each subsequent workout during the supercompensation phase. The moment of its onset depends on the condition of the muscles and the intensity of the training. The stronger and larger the muscles, the longer they take to recover. Therefore, the optimal training frequency should be calculated very responsibly.
The supercompensation phase, in most cases, occurs 6–7 days after the lesson. Therefore, theoretically, the frequency of strength training should not exceed 1 - 2 per week. This is precisely the regime that some experts insist on.
However, other experienced athletes and coaches encourage visiting the gym literally every day. As proof, they demonstrate their own results, assuring that it is possible to build muscle with a high frequency of training.
Having become familiar with such contradictory information, a novice athlete may become confused. Therefore, it is advisable to consider how strength training and mass training programs are built in practice. It is important to remember that high frequency of strength training can lead to overtraining.
Optimal frequency to ground

Having studied the theoretical recommendations regarding the construction of a training program, let’s move directly to practice. Exercising once a week is ineffective, and if you exercise every day, you risk harming your body. Let's consider an option that will be safe and useful for a bodybuilder.
According to practitioners, the optimal frequency of weight training should be 3 – 4 times a week. Moreover, the athlete should train according to a split program, working specific muscle groups every day. That is, in fact, the same muscles receive load 1-2 times a week - directly in the supercompensation phase.
Optimal drying frequency

If you want not so much to build muscle as to emphasize your relief and lose weight, it is permissible to train more often. The best option is 4 or 5 times a week. Some people can exercise every day - the main thing is not to overdo it and avoid overtraining.
A person interested solely in losing excess weight can exercise almost daily, preferring aerobic exercise. Use cardio exercises, work with high intensity and light weights. The result will not keep you waiting!
If your goal is drying and creating relief, it is recommended to do strength training with a predominance of anaerobic exercises once a week. Dedicate all other days to cardio exercises. Thanks to this approach, you will lose less muscle mass, while at the same time getting rid of the fat layer that hides the relief. The frequency of training per week is often selected individually, based on the capabilities and needs of the athlete.

 If training is carried out very often, the muscles will not have time to recover. This will only make your situation worse, and each subsequent session will gradually lead to overtraining and stagnation. Also, frequent training may be part of a training plan (as with split training), at which time the muscles will become more tired than usual and require a longer time to recover. For example, some professional athletes train 6 days a week, but according to a split program, that is, in any case, each muscle group will have enough time to recover. Therefore, frequent training can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on what program you are training in (full body, split, top-bottom, etc.).
If training is carried out very often, the muscles will not have time to recover. This will only make your situation worse, and each subsequent session will gradually lead to overtraining and stagnation. Also, frequent training may be part of a training plan (as with split training), at which time the muscles will become more tired than usual and require a longer time to recover. For example, some professional athletes train 6 days a week, but according to a split program, that is, in any case, each muscle group will have enough time to recover. Therefore, frequent training can be both beneficial and harmful, depending on what program you are training in (full body, split, top-bottom, etc.). Scientific studies have shown that muscle recovery requires an average of two days, and the peak period of supercompensation occurs only 6-7 days after a good workout. Based on this information, we can say that the optimal frequency of training is once a week for each individual muscle group. Since most athletes train 2-3 muscle groups per workout, it is best to do 3-4 workouts per week.
Scientific studies have shown that muscle recovery requires an average of two days, and the peak period of supercompensation occurs only 6-7 days after a good workout. Based on this information, we can say that the optimal frequency of training is once a week for each individual muscle group. Since most athletes train 2-3 muscle groups per workout, it is best to do 3-4 workouts per week.

















